Is the JRS Eco router compatible with my Internet provider / Internet gateway box?
Our Eco routers are compatible with every Internet provider and every Internet modem/router. You need an Internet box (router/modem) from your provider. This is because our Eco routers are separate wifi routers, not modems, so a modem is required for the connection to your provider. You connect the Eco-Router to your Internet box with the network cable supplied by using the standard LAN connection, which is available on every Internet modem/router.Turning off the Wi-Fi of the internet modem
If your Internet gateway box has built-in wifi, this needs to turned off in order to minimize wifi radiation and interference. See 'How do I turn off the Wi-Fi of my provider's Internet gateway box?' The provider should always allow you to disable the wifi. (For example, some people have a gaming router, which they want to let take over the wifi.) Usually you can easily find with google how to do it. We can help you disable the wifi if you let us know the make and model of your internet modem.Which JRS Eco router model should I choose?
In short, do you want Wi-Fi in just one room? Then choose the D2 model with the optional attenuators. Otherwise, opt for the D1 model. Without attenuators, the D2 has the same range as the D1.- The JRS Eco 100 D2 has removable antennas, making it possible to deploy the optional attenuators. This reduces the range of the D2 to about 10 meters, reducing radiation even further, to e.g. only one room.
- The D2 is an upright model, and the D1 is a tabletop model. The D1 has 2 screw holes for wall mounting on the bottom.
- The JRS Eco 100 D2 has a separate WPS on/off push button on the side. On the D1, the WPS button functions as a wifi on/off push button.
| JRS Eco 100 D1 on Asus - Low EMF wireless router | JRS Eco 100 D2 on Asus - Low EMF wireless router | |
| Full Eco Zero Emission stand-by mode | ||
| 90% reduced beacon pulse frequency | ||
| Fine adjustment of range with 1 milliwatt step size | ||
| Wifi time-switch - Set times when wifi automatically switches off 100%, e.g. at night | ||
| On/off switch for wifi transmitter - cabled LAN ports keep functioning | ||
| Detachable antennas, option for inserting extra attenuators | - | |
| Suitable for wall mounting | - | |
| Dual band (extra channels at 5 Gigahertz) | ||
| AC wifi for super high speed | ||
| Max. throughput speed on 2.4 GHz wifi network measured with Speedtest.net | 150 Mbps | 150 Mbps |
| Max. throughput speed on 5 GHz wifi network measured with Speedtest.net | 400 Mbps | 400 Mbps |
| Speed for normal internet usage (browsing websites) | +++ | +++ |
| Range and number of external antennas | +++ (3) | +++ (3) |
| Asus router type | RT-AC66U B1 | RT-AC68U |
| Dimensions (mm) | 218 x 148 x 45 | 220 x 83 x 160 |
| Firewall and WPA2-security with password | ||
| Gigabit ethernet LAN ports | ||
| Two USB ports for sharing USB storage and print server | ||
| VPN client and server | ||
| Guest networks |
How do I turn off the Wi-Fi of my provider’s Internet gateway box/router?
If you want to reduce the Wi-Fi radiation in your home, you should know that most of it comes from your Internet gateway box/router/modem, which in most cases you get from your provider. How can you turn off this Wi-Fi and connect your own router, such as a Low-EMF JRS-Eco Router? In most instances, you cannot simply replace your Internet modem/router/box with an Eco-router. This is because you need the Internet router to convert the Internet signal, which enters the house via another type of connection (e.g. cable or fiber optic), to an Ethernet port. The Eco-router can then be connected to this. Most Internet gateway boxes have built-in Wi-Fi. It must be switched off to get rid of its radiation and to avoid interfering with the Eco router's network. You no longer need the Internet modem's Wi-Fi, because the Wi-Fi function is taken over by the Eco router, with much less EMF! This gives you peace of mind and control over the Wi-Fi radiation in your home. The phone and TV continue to work as normal when connected to the internet router, as it just stays put. Below are instructions on how to disable Wi-Fi for the most common providers: Other providers On some Internet routers/modems, you can simply turn off the Wi-Fi with a switch on the device. Otherwise, it is done by logging into a settings menu that can be accessed through a browser by entering the correct address (the IP number), which is often listed on the bottom of the modem/router. In most cases, you can find a do-it-yourself guide on the Internet by Googling the name of your ISP and the make and model of your Internet modem, e.g. "Disable Wi-Fi AT&T BGW320 router". If this doesn't work for you, you can try contacting your provider's customer service for help.Can I use the Eco router together with my Wi-Fi booster? How many routers/extenders do I need?
Do you currently have a system with wireless extenders/repeaters or a mesh? A mesh is a mess from an EMF point of view. All wireless signals are transmitted twice or more from one mesh node to another. Wi-Fi repeaters have a similar problem. It’s like a Wi-Fi receiver and access point in one box. Each Wi-Fi repeater will transmit 10 pulses per second, 24 hours per day. Furthermore, we cannot guarantee seamless interoperability of our Eco routers with a repeater. We recommend that you run a LAN cable to the 2nd, 3rd point and so on where you need Wi-Fi and put another Eco router there. For more information, see Is a wifi booster/repeater/extender a good idea in terms of radiation? The range you get from an Eco router is the same as you would get from an ordinary router. It's hard to say how many you'll need without knowing the exact situation, but a safe bet would be to assume that you need as many Eco routers as you currently have Wi-Fi routers and repeaters combined. So, would it be it an option for you to run Ethernet cables to all the places where you need a router? If you can do this, it will significantly reduce your exposure to EMF in your home compared to the situation with repeaters.How to install your Eco router – video manual
Easy installation. The Eco-WiFi router is connected to your internet modem using a standard network cable (included). If your internet modem has built-in Wifi, switch off its Wifi function. You may ask your internet provider’s customer service how. All functions of your existing internet modem, like for example internet telephony, can still be used.
The exposure to EM radiation from the laptop or other wirelessly connected equipment remains unchanged. Set your smartphone to switch its wifi off in stand-by mode. In some cases you can reduce the transmit power of your computer’s WiFi adapter using the Device Manager in Windows. A wired internet connection is radiation-free and minimizes health risk.
The JRS Eco 100 wireless router: 100% radiation-free in stand-by
 An ordinary wifi router broadcasts beacon signals 24 hours a day, 10 times a second. This generates a considerable amount of radiation in the home, clearly measurable. The unique JRS® Eco 100 wireless router automatically switches to Full Eco stand-by mode, reducing radiation to zero, when you turn off wifi on your computer and phone. When you reconnect to the wifi, the JRS Eco 100 router automatically switches the signal on again. What makes these Asus® routers special is the JRS Eco firmware that runs on them. The first generation of JRS Eco wireless routers already significantly reduced the amount of electrosmog by reducing the pulse frequency of the beacon signals by a factor of 10. See Eco router: 90% reduced pulse frequency. The JRS Eco 100 technology takes it one step further.
An ordinary wifi router broadcasts beacon signals 24 hours a day, 10 times a second. This generates a considerable amount of radiation in the home, clearly measurable. The unique JRS® Eco 100 wireless router automatically switches to Full Eco stand-by mode, reducing radiation to zero, when you turn off wifi on your computer and phone. When you reconnect to the wifi, the JRS Eco 100 router automatically switches the signal on again. What makes these Asus® routers special is the JRS Eco firmware that runs on them. The first generation of JRS Eco wireless routers already significantly reduced the amount of electrosmog by reducing the pulse frequency of the beacon signals by a factor of 10. See Eco router: 90% reduced pulse frequency. The JRS Eco 100 technology takes it one step further. How does the Eco 100 router work?
Only when one of your wifi devices sends a wifi connection request does the JRS Eco 100 router immediately turn on the wifi signal. This means it only switches on for devices that belong to you. Your wireless device sends such a connection request when you switch on the wifi slider or open the list of available wifi networks. This is automatic and you won't notice any difference with a regular wifi router. When you install the JRS Eco 100 router, it first goes into learning mode so you can easily connect all your devices. The router automatically keeps a list of your devices that have been connected to it. Once all your devices are listed, the router automatically switches to Full Eco mode, in which it is completely radiation-free when no wifi devices are connected to it.  |
 |
Measurements
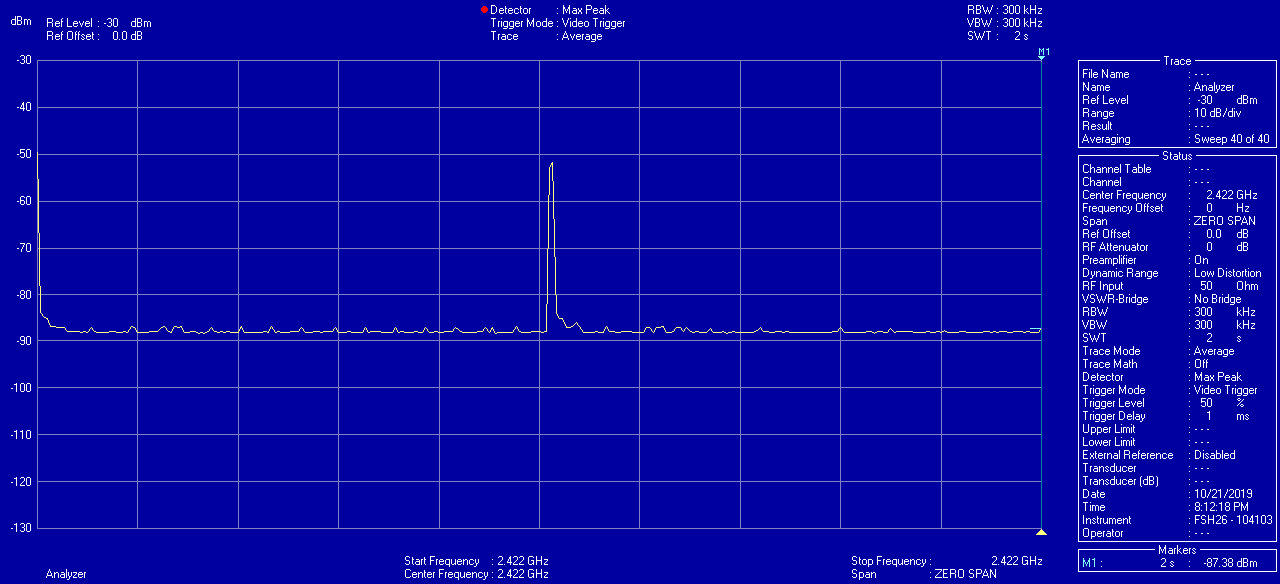
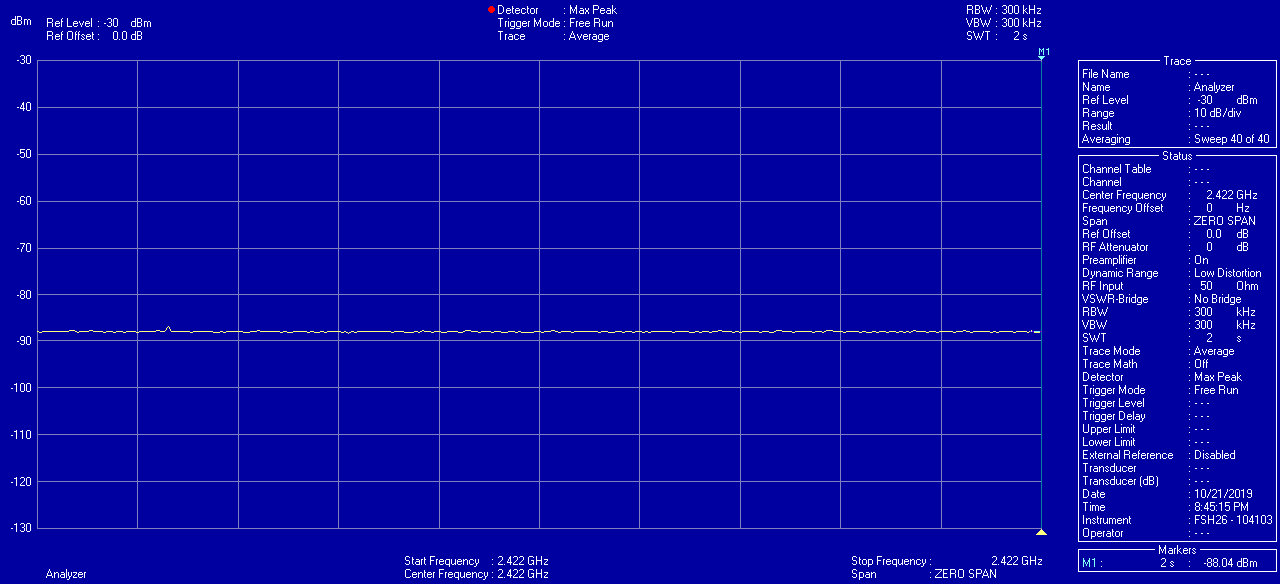
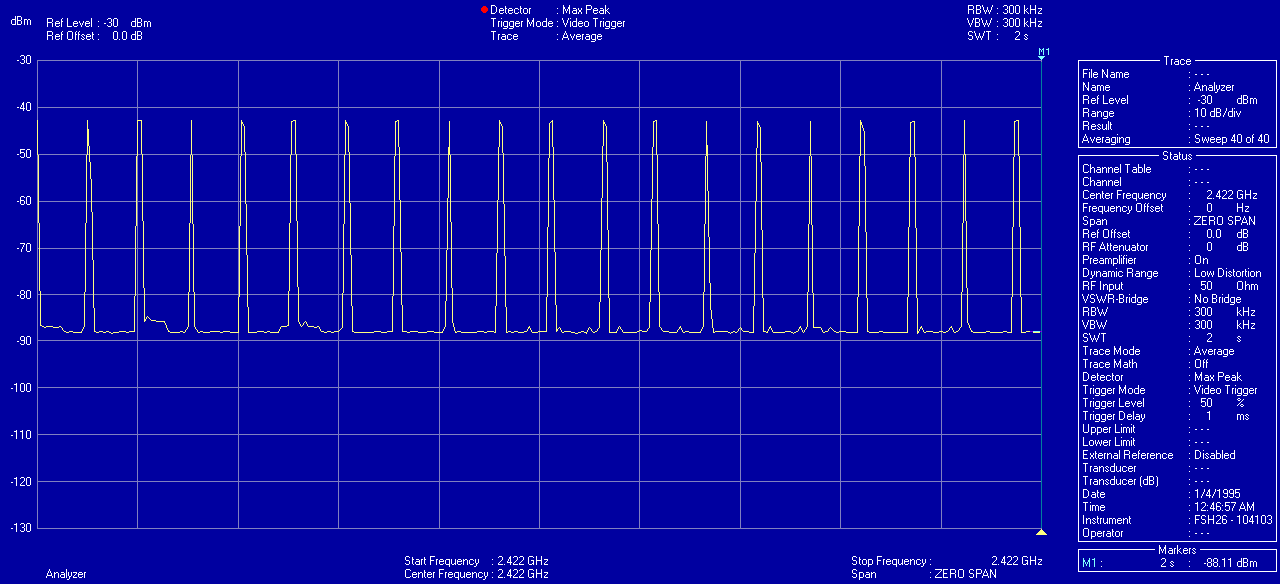
Can I accomplish the same by adjusting the settings in an ordinary router?
The JRS Eco 100 functionality, which automatically turns off the wifi signal completely in stand-by, is unique to the JRS Eco 100 operating system and is not available on ordinary routers. People sometimes think that by setting a "Hidden SSID" on a regular wifi router, they reduce radiation. This is a misconception. With a 'packet sniffer' program like Wireshark you can determine that the router is still transmitting beacon packets, only the so-called 'SSID' field in these packets is set to zero. It doesn't reduce radiation from the router in any way. What about other settings? Often you can't adjust the transmitting power in ordinary routers or only in rough steps. The JRS Eco 100 firmware offers fine tuning of the transmission power with 10 steps, which is not available in the regular Asus® firmware.To what extent does an Eco router reduce my exposure to wifi radiation?
Wifi is two-way traffic. Although the Eco router greatly reduces the radiation of your router during stand-by and partly during operation, it does not reduce the radiation of your wireless devices. For each piece of data sent from the wifi router, a confirmation is sent back by your device. Wifi radiation from the devices is very strong and you keep the device very close to your body. Especially in data-intensive applications such as video, a lot of wifi radiation is emitted. By working with a wired Internet connection, you can minimize your exposure to electromagnetic radiation. See also the iPad® / iPhone® hardwired adapter.Eco router: 90% reduced pulse frequency
Even when the Eco router is in use, with devices connected, it emits less radiation than an ordinary wifi router. The Eco router has a 10x reduced beacon pulse frequency. This is explained below. Any wifi router transmits two main types of packets:- Beacon packets containing the name of the wifi network. The largest problem is, that in ordinary wifi routers, these are transmitted 10 times per second 24/7, both in standby and during usage. The Eco router reduces the pulsation frequency of this beacon signal to once per second.
- Data packets. Data packets are only transmitted during usage, for example when loading a web page, when an app is requesting information from the internet, or your device is downloading updates etc.
Measurements
This is measurable using an electrosmog meter. The reduced pulse frequency of the beacon signal in the Eco routers has been measured by EMF Consult Norway. The oscilloscope images below show the measured electromagnetic emission versus time, on a 200 milliseconds x-axis scale. The left image shows an ordinary wifi router, and the right image shows the Eco router: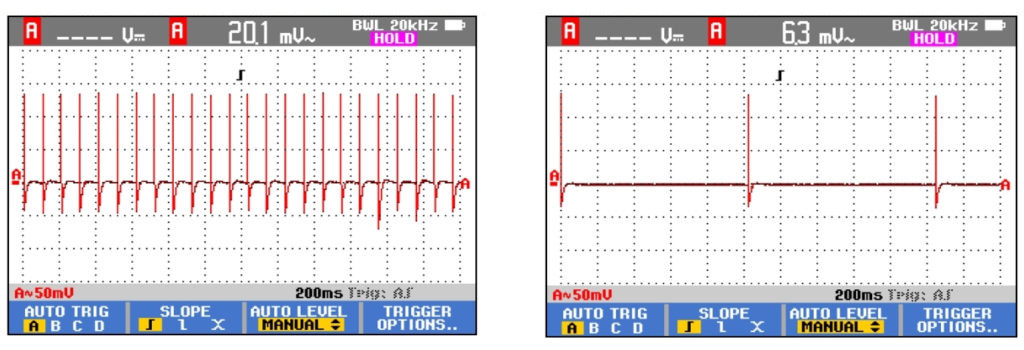 A demonstration is given in the below video from ElectricSense.com, measured with an Acoustimeter. Turn on sound to hear the difference:
A demonstration is given in the below video from ElectricSense.com, measured with an Acoustimeter. Turn on sound to hear the difference: 





